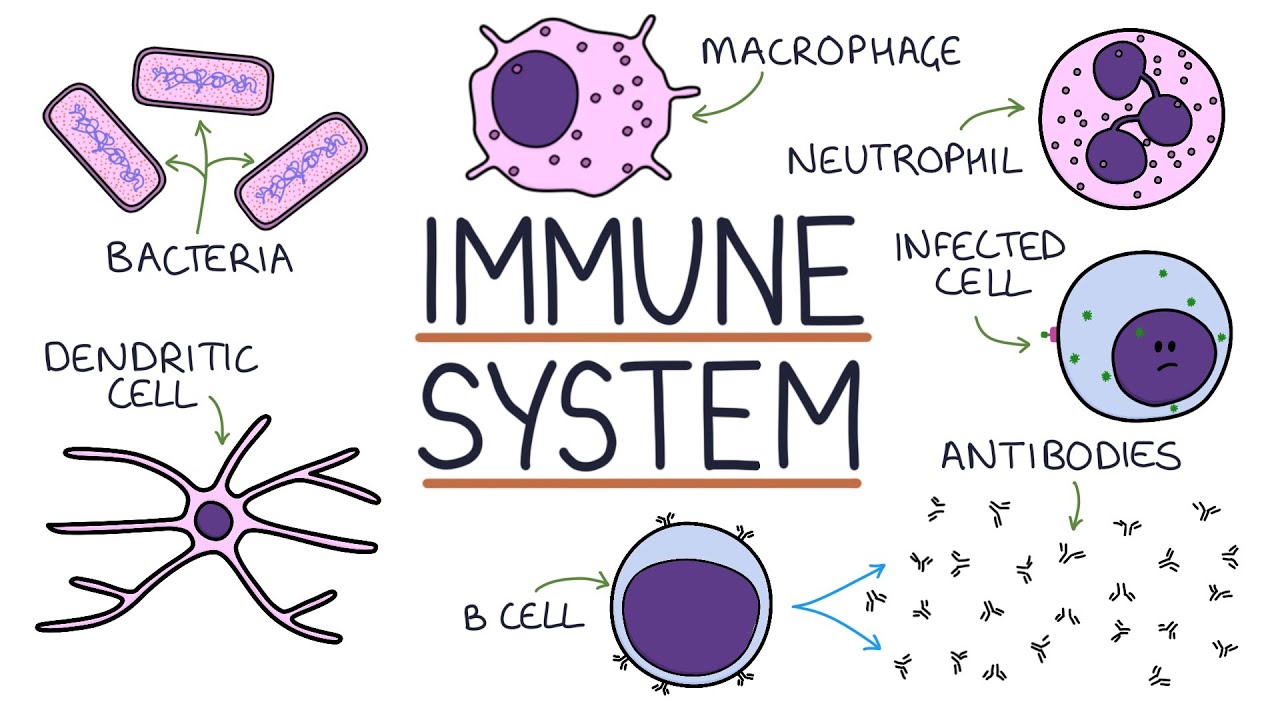
Introduction
Your immune system is a remarkable network of cells, tissues, and organs that tirelessly defends your body against a vast array of invaders. It’s your biological shield, protecting your health and well-being. Understanding this complex system is key to recognizing its importance and how to support a strong immune response.
Components of the Immune System
The immune system is divided into two main branches:
- Innate Immune System: Provides a rapid, non-specific defense against a broad spectrum of pathogens (germs). It includes:
- Physical barriers: Skin, mucous membranes, stomach acid.
- Immune cells: Phagocytes (engulf invaders), natural killer cells (destroy infected cells).
- Inflammation: An early response to injury or infection.
- Adaptive Immune System: Mounts a targeted, long-lasting response against specific pathogens. Key components:
- Lymphocytes: White blood cells including B cells (produce antibodies) and T cells (coordinate immune responses).
- Antibodies: Proteins that bind to specific antigens (foreign substances on pathogens) and mark them for destruction.
- Memory Cells: Long-living cells that “remember” past encounters, boosting the response upon reinfection.
How the Immune System Functions
- Identifying Invaders: The immune system constantly identifies and attacks foreign substances using surface proteins called antigens.
- Launching an Attack: The innate system swiftly deploys immune cells to the site of infection and triggers inflammation to contain the threat.
- Adaptive Response: If the initial response is insufficient, the adaptive system activates. Antibodies target the specific pathogen, and T cells coordinate a specialized attack.
- Memory Creation: Once the threat subsides, memory cells remain, ready to rapidly counter future infections by the same pathogen.
Factors Influencing the Immune System
- Age: The immune system is typically strongest in young adulthood, with some decline in function with age.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in key nutrients like vitamins C, D, and zinc supports immune health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can suppress immune function.
- Sleep: Inadequate sleep impairs immune response.
- Exercise: Regular exercise promotes immune health, but excessive exercise can create temporary suppression.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Chronic diseases or immune deficiencies compromise immune function.
- Medications: Certain medications, like corticosteroids, can suppress the immune system.
Signs of a Weakened Immune System
- Frequent infections (colds, flu, etc.)
- Slow wound healing
- Persistent fatigue
- Digestive issues
- Skin problems
Boosting Your Immune System
While you can’t directly control your immune system, healthy lifestyle choices support its function:
- Nutritious Diet: Prioritize whole foods, especially fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
- Quality Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of restful sleep nightly.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can impair immune function.
- Limit Alcohol and Smoking: These habits weaken immune response.
- Supplements (with Healthcare Provider Guidance): Vitamins D, C, and zinc may offer support.
The Importance of the Immune System
A strong immune system is essential for:
- Fighting Infections: Protects against bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Cancer Prevention: Detects and eliminates abnormal cells before they multiply.
- Wound Healing: Promotes tissue repair and recovery after injury.
Important Notes:
- Autoimmune Disorders: These occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues.
- Vaccinations: Prime the immune system with a tailored “preview” of a pathogen, strengthening subsequent defenses.
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss significant concerns about your immune health with a healthcare professional.